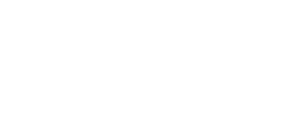If we have to mention one of the most common and dangerous issues in influencer marketing, we’d say it’s influencer fraud. It isn’t always easy to see right away, but the outcome is always hard to miss. Weeks or months of working with influencers can end with disappointing sales or weak content performance due to fraud. The part that hurts the most is, manual ways aren’t very convenient and effective, and it’s hard to decide where to start tracking, especially for busy or beginner marketers.
This problem is one of the reasons why HypeAuditor was built in the first place. From the start, we’ve always been focused on protecting brands and agencies by spotting fraud. The AI-powered HypeAuditor analyzes influencers across platforms and is able to catch different kinds of fraud with high accuracy, proven by tests showing that 95.5% of known fraudulent activity can be detected by HypeAuditor. By combining accuracy with transparency, HypeAuditor makes influencer marketing safer for every collaboration.
What makes this more convenient is that all of the insights come together in a single report for every influencer. So, marketers can access and reveal what’s behind every curtain without having to spend hours searching through different tools and notes. These reports cover all the important analytics in a way that’s both easy to read and thorough, so teams at different levels of expertise can understand the data without losing its depth or value.
In this article, we’ll look at the main types of fraud in influencer marketing, how they work, and how HypeAuditor helps you deal with them.
1. Fake followers
Fake followers are purchased accounts that make an influencer’s audience look bigger than it really is. These followers are usually bots or inactive profiles created in bulk and sold through third-party services. They don’t watch content, click links, or make purchases, yet they pump up follower counts to create the illusion of popularity. At a glance, an influencer may look like they have a large community, but when you see their actual post reach and content impact, it’s far smaller than the number suggests. This is because the presence of fake followers doesn’t add up to anything.
 HypeAuditor addresses this problem with an AI model trained on more than 53 behavioral patterns that flag low-quality or suspicious followers. The platform breaks down every influencer’s audience into four clear groups:
HypeAuditor addresses this problem with an AI model trained on more than 53 behavioral patterns that flag low-quality or suspicious followers. The platform breaks down every influencer’s audience into four clear groups:
Real people: active, real users who can actually engage with content.
Influencers: accounts with more than 5,000 followers.
Mass followers: users who follow more than 1,500 accounts. Since their feeds are overloaded, they rarely see or interact with influencer posts. Many use automated follow/unfollow tactics.
Suspicious accounts: bots or users who rely on automation to artificially increase likes, comments, or follower counts. Any account showing “grey hat” activity falls here.
 Another important highlight, HypeAuditor provides an Audience Quality Score (AQS), a proprietary metric on a scale of 1 to 100. To score each influencer, it combines factors such as audience credibility, engagement authenticity, and growth patterns into a single number. With AQS, marketers can quickly understand how reliable an influencer’s audience is before making a decision.
Another important highlight, HypeAuditor provides an Audience Quality Score (AQS), a proprietary metric on a scale of 1 to 100. To score each influencer, it combines factors such as audience credibility, engagement authenticity, and growth patterns into a single number. With AQS, marketers can quickly understand how reliable an influencer’s audience is before making a decision.
This not only reduces the risk of working with influencers who have fake followers, but also makes it easier to interpret audience quality and engagement in a way that anyone can understand, whether you’re new to influencer vetting or already experienced.
2. Strange patterns of follower growth
Unusual follower growth is when an influencer’s audience count spikes suddenly without a clear reason. This often points to purchased followers and doesn’t line up with how genuine communities grow over time. These irregular surges rarely match the influencer’s engagement levels, which makes the account look suspicious.
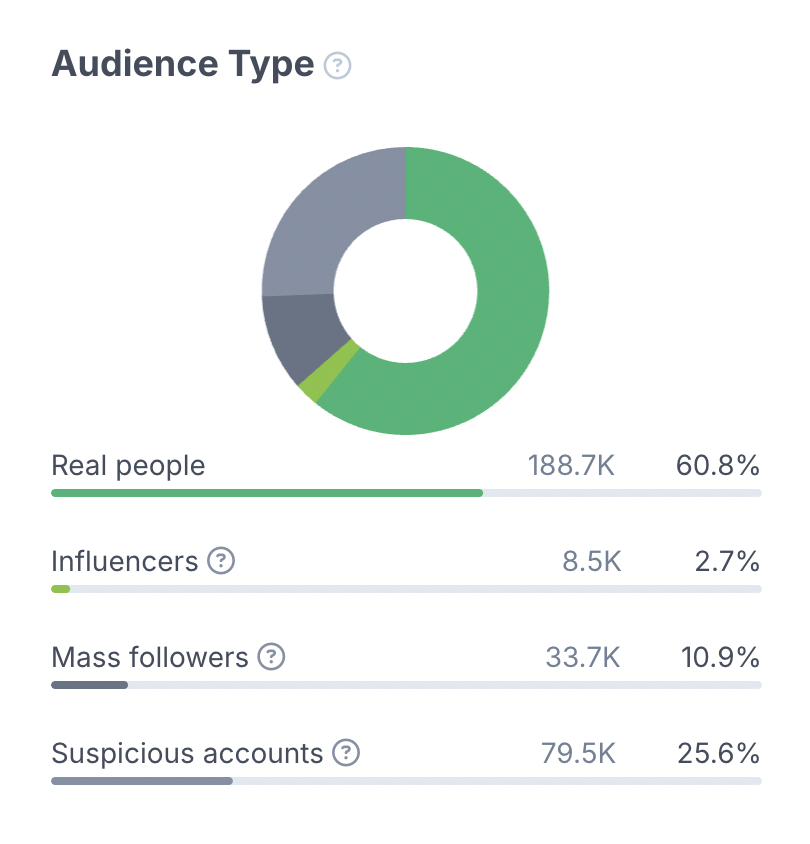
 HypeAuditor helps marketers spot this kind of pattern by showing a detailed history of follower growth on platforms like Instagram and TikTok. Each account has a graph that tracks daily gains and losses from the very beginning, so you can see if the growth trend is steady or volatile. Sudden jumps, sharp drops, or long flat lines are all red flags, and the platform highlights them directly on the chart. For example, if there’s a spike followed by a long period of decline, HypeAuditor will flag it as abnormal growth. This makes it easier to judge when an influencer’s audience is growing authentically and when the pattern suggests any involvements of artificial methods.
HypeAuditor helps marketers spot this kind of pattern by showing a detailed history of follower growth on platforms like Instagram and TikTok. Each account has a graph that tracks daily gains and losses from the very beginning, so you can see if the growth trend is steady or volatile. Sudden jumps, sharp drops, or long flat lines are all red flags, and the platform highlights them directly on the chart. For example, if there’s a spike followed by a long period of decline, HypeAuditor will flag it as abnormal growth. This makes it easier to judge when an influencer’s audience is growing authentically and when the pattern suggests any involvements of artificial methods.
3. Engagement pods & fake interactions
Pods are groups of creators who agree to like and comment on each other’s posts in order to artificially grow engagement. Sometimes these are small private groups, other times they are paid services designed to trick algorithms and brands into believing the content is performing better than it really is. The activity looks like real engagement on the outside, but it doesn’t reflect genuine audience interest. For brands, this is a proof that even data can be misleading, and partnerships risk being built on false signals without deeper examination.
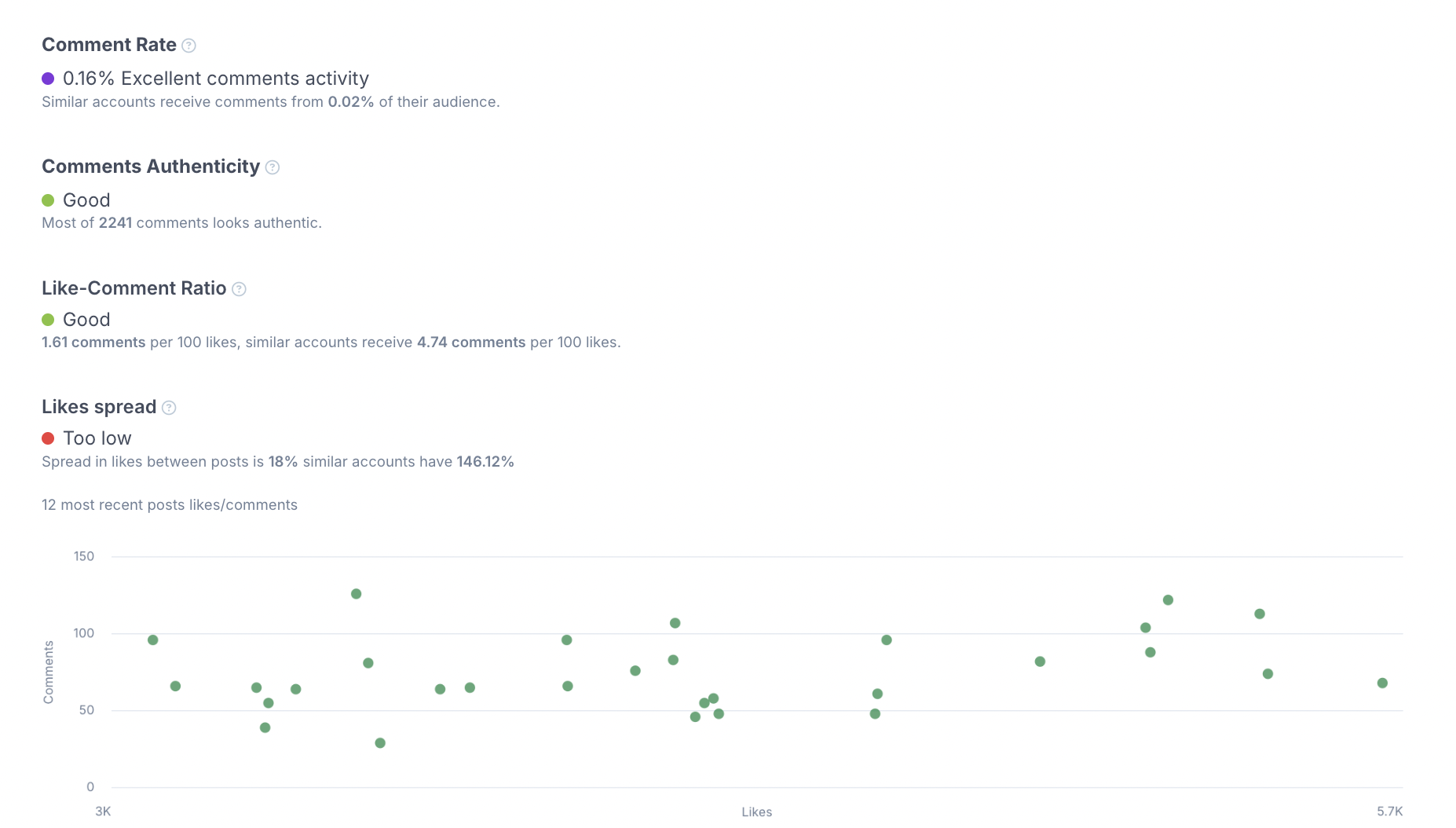 HypeAuditor’s approach to preventing that is through comment authenticity analysis, which looks at two main factors: the quality of the account leaving the comment and the content of the comment itself. A comment is flagged as inauthentic if both factors are concerning.
HypeAuditor’s approach to preventing that is through comment authenticity analysis, which looks at two main factors: the quality of the account leaving the comment and the content of the comment itself. A comment is flagged as inauthentic if both factors are concerning.
Some patterns of suspicious accounts’ activities can include purchased likes, spam hashtags, or other automation techniques. Meanwhile, inauthentic content often includes:
Emoji-only replies or generic words like “wow” or “cool”
Comments about giveaways or contests
Repeated patterns that suggest pod activity
When several of these watchful signs appear together, HypeAuditor marks the comment as inauthentic. This helps marketers separate real community reactions from artificial ones and gives a more accurate view of how an influencer’s content actually resonates with their audience.
4. Inauthentic comment activity
The amount of comments isn’t always a true signal of engagement. There are influencers who buy comments or use bots to create activity that looks credible. These often appear as short, repetitive phrases like “Nice pic!” or just strings of emojis. In other cases, brands encounter buzzer accounts—profiles with very few followers or posts that exist mainly to leave fake comments. All of this creates the impression of an active audience, while in reality there’s little genuine interaction.
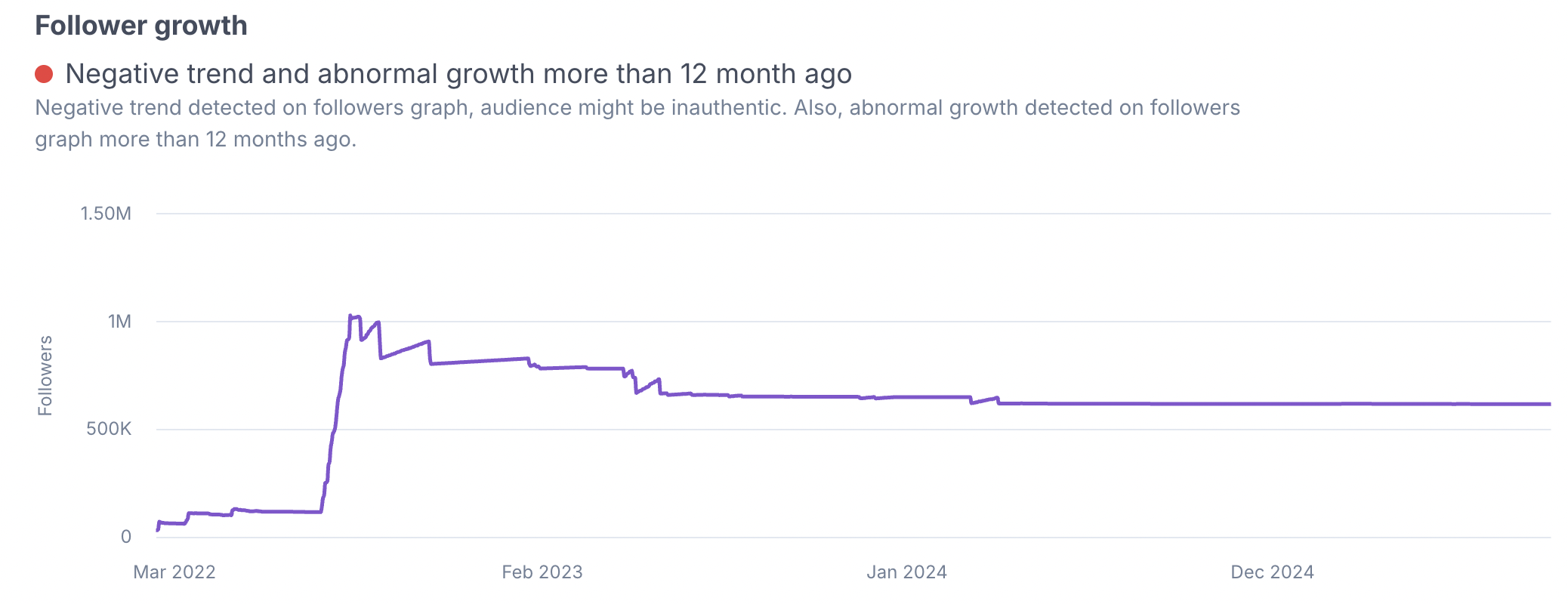
HypeAuditor helps detect this fake engagement using Comments Authenticity analysis and the Like-Comment Ratio. The Comments Authenticity reviews each comment based on the content and the credibility of the accounts posting them. If replies are filled with spammy patterns or come from suspicious accounts, they’re flagged as inauthentic.
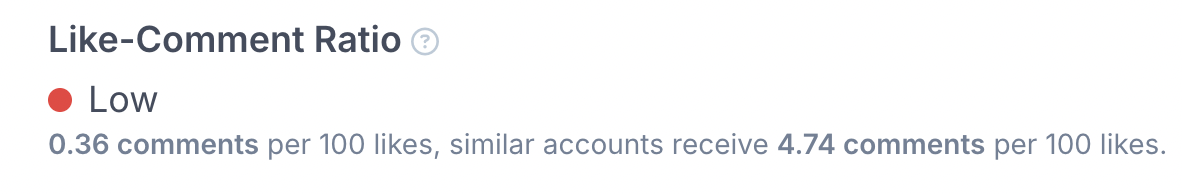 The Like-Comment Ratio then shows how many comments an influencer typically receives per 100 likes compared with similar accounts. Large differences often indicate that the comments were artificially blown up.
The Like-Comment Ratio then shows how many comments an influencer typically receives per 100 likes compared with similar accounts. Large differences often indicate that the comments were artificially blown up.
If the report shows comment activity that doesn’t match expected patterns, it signals low-quality engagement. In these cases, it’s worth rethinking whether the influencer can deliver the kind of audience interaction your campaign needs.
5. Audience misrepresentation
Sometimes influencers present their audience in a way that doesn’t match reality. They might claim their followers are mostly from the US, but analytics show the majority are based elsewhere. Or they may give the impression of having a strong base in a certain age group, while in fact most of their audience falls into another. These mismatches can misdirect brands into targeting the wrong market and splurging resources on poorly fitted collaborations.
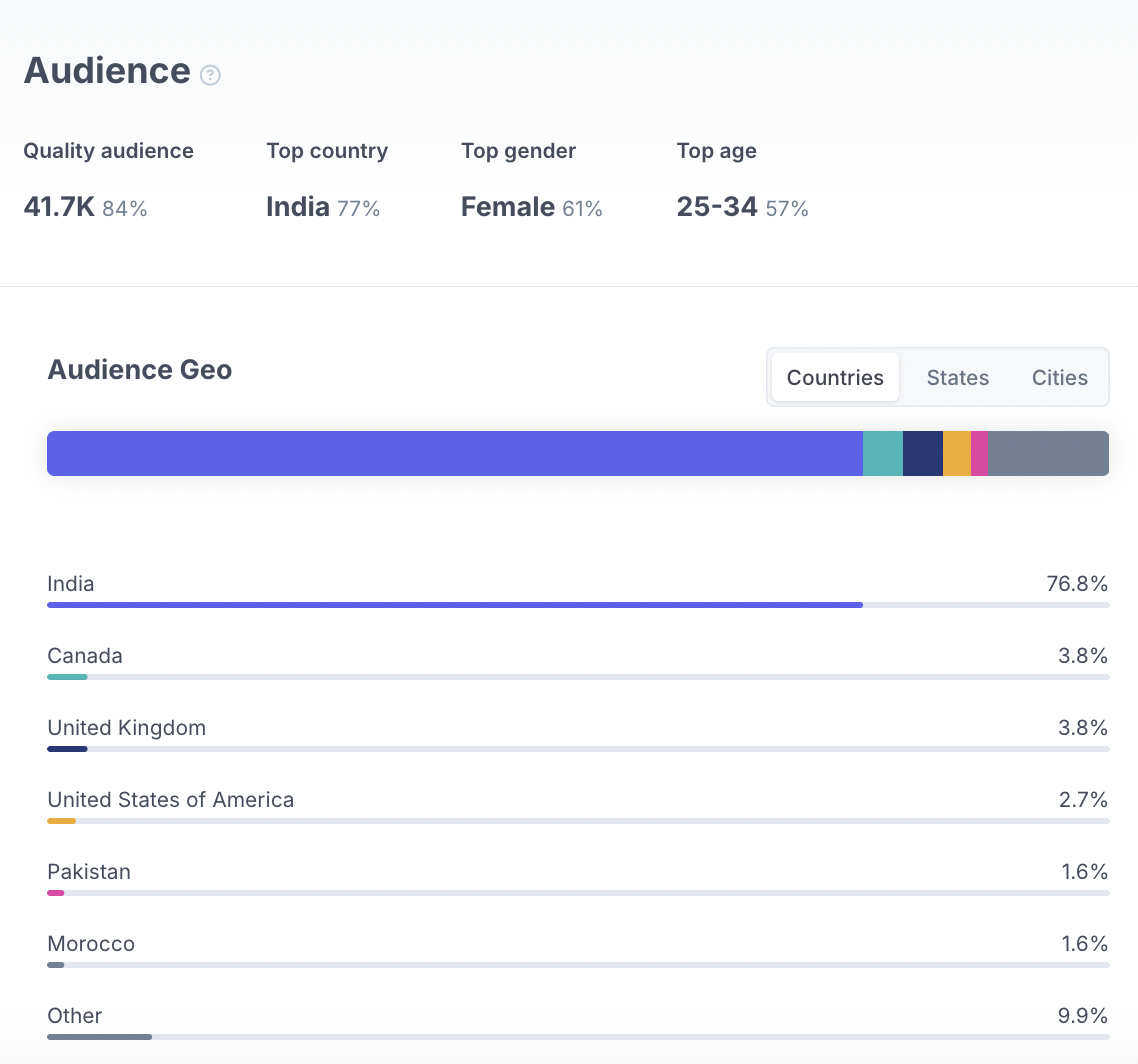 But this can still be prevented using HypeAuditor, as it provides a full breakdown of audience demographics and sociographics in every influencer report. In the Audience section, marketers can instantly see the number of quality followers, along with the top country, gender, and age group. The data can also be broken down by states and cities for more precise targeting.
But this can still be prevented using HypeAuditor, as it provides a full breakdown of audience demographics and sociographics in every influencer report. In the Audience section, marketers can instantly see the number of quality followers, along with the top country, gender, and age group. The data can also be broken down by states and cities for more precise targeting.
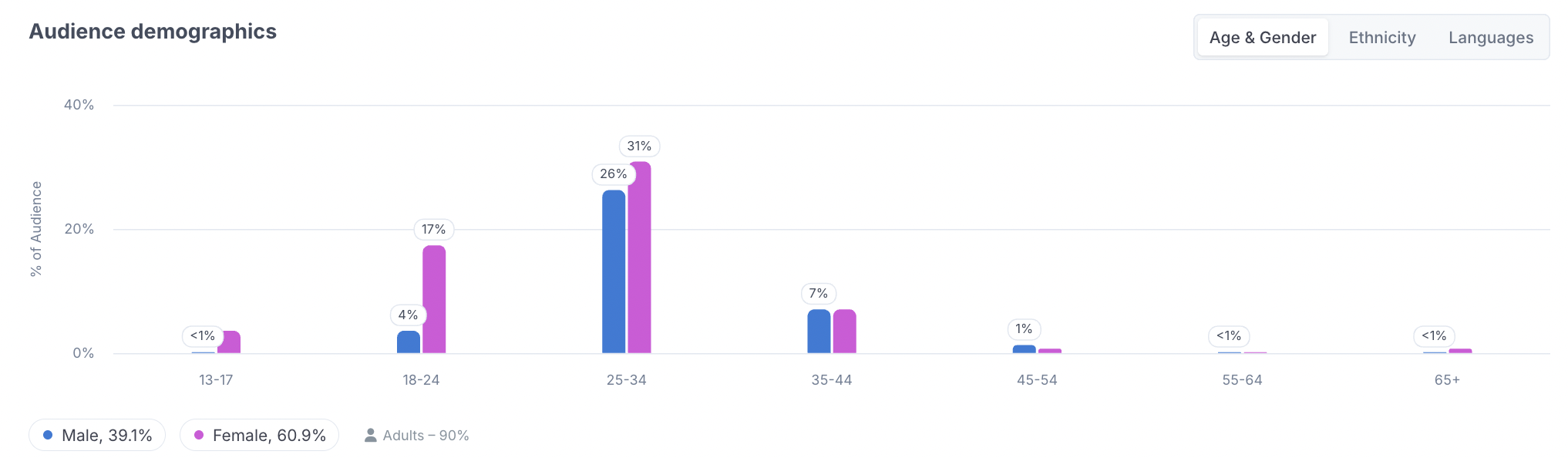 Other than this overview, the platform offers detailed demographic charts including age and gender distribution, ethnicity, and languages spoken. These insights help brands understand not only how large an influencer’s audience is, but also how relevant it is for a specific campaign.
Other than this overview, the platform offers detailed demographic charts including age and gender distribution, ethnicity, and languages spoken. These insights help brands understand not only how large an influencer’s audience is, but also how relevant it is for a specific campaign.
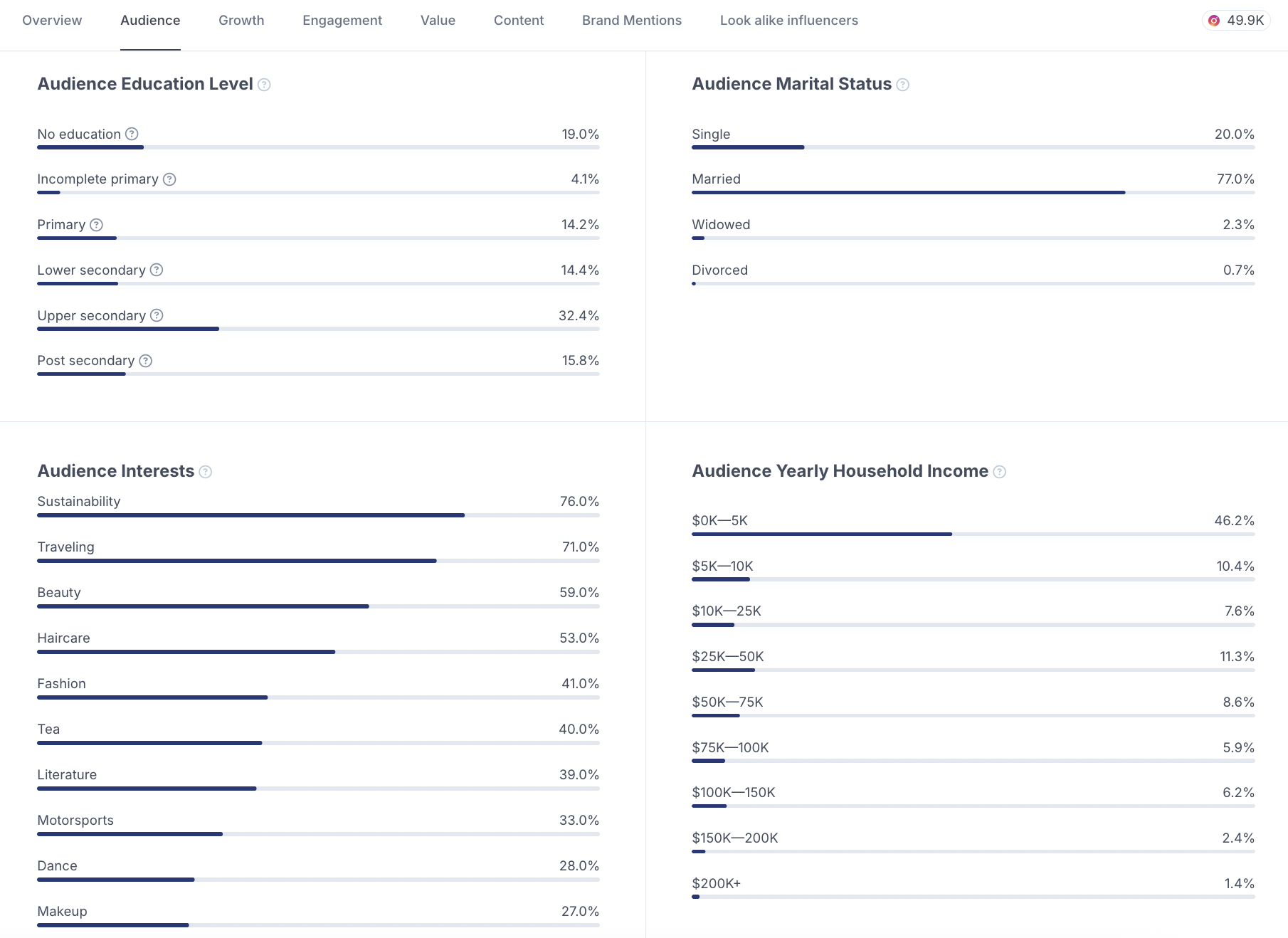 HypeAuditor also adds sociographic breakdowns that reveal more about the background of an influencer’s audience:
HypeAuditor also adds sociographic breakdowns that reveal more about the background of an influencer’s audience:
Education Level: the spread of followers across different education levels.
Marital Status: the proportion of single, married, widowed, or divorced followers.
Audience Interests: categories like beauty, travel, sustainability, or fashion, with followers often belonging to more than one.
Yearly Household Income: audience’s annual income estimated by AI models based on age, gender, and location, presented in US dollars.
By combining demographic and sociographic insights, marketers can judge more wisely whether an influencer’s community is the right fit. This allows you to be very sure that the campaigns reach the right people with relevant interests, and within a realistic spending capacity.
6. Fake collaborations
Tagging a brand doesn’t always mean there’s a real partnership behind it. In fact, influencers may mention companies in their posts to make themselves look more established and in demand. To followers, it creates the impression of credibility, and to potential partners, it suggests a history of successful campaigns. In reality, these tags can be nothing more than self-promotion, with no actual collaboration involved. That’s why brands need to verify partnerships carefully before assuming the relationship is real.
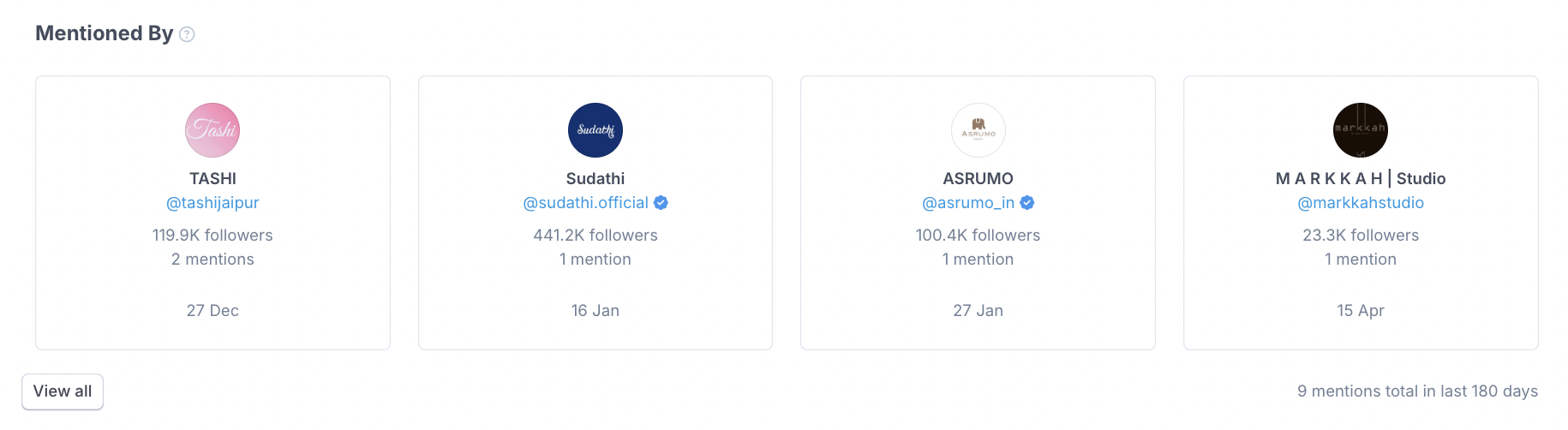 To help marketers avoid this, HypeAuditor includes the Mentioned By section. This shows which accounts have tagged or mentioned the influencer in the last 180 days. It helps explain growth trends (such as mentions through giveaways or promos) and gives you context on whether the brands tagged actually represent partnerships.
To help marketers avoid this, HypeAuditor includes the Mentioned By section. This shows which accounts have tagged or mentioned the influencer in the last 180 days. It helps explain growth trends (such as mentions through giveaways or promos) and gives you context on whether the brands tagged actually represent partnerships.
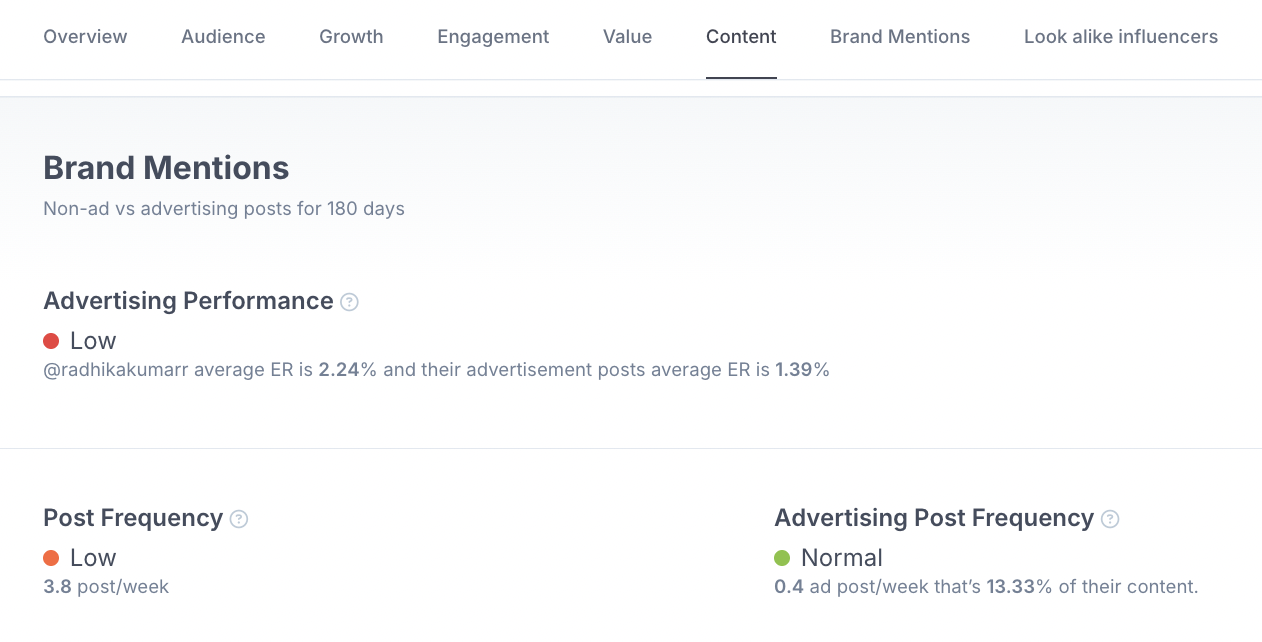 The Brand Mentions section provides details about how often an influencer works with paid collaborations and how those posts perform compared to regular content. This enables you to see the difference between casual brand tags and real, existing partnerships.
The Brand Mentions section provides details about how often an influencer works with paid collaborations and how those posts perform compared to regular content. This enables you to see the difference between casual brand tags and real, existing partnerships.
The Advertising Performance metric compares the engagement rate of regular posts with posts that include brand mentions. If engagement is higher on branded posts, it shows the influencer is able to promote products in a way that resonates with their audience.
Finally, the Advertising Post Frequency metric shows how often an influencer publishes content with brand mentions. If their feed is overloaded with sponsored posts, it may be a sign to reconsider. Still, not every mention is promotional; sometimes creators tag products they genuinely use and like.
7. Manipulated performance reports
Unfortunately, there are influencers who try to fabricate their campaign results by sending edited screenshots of impressions, clicks, or sales. These numbers might look convincing at first, but actually, they don’t reflect reality. Without proper verification, brands risk basing their decisions on manipulated data that hides an influencer’s true performance.
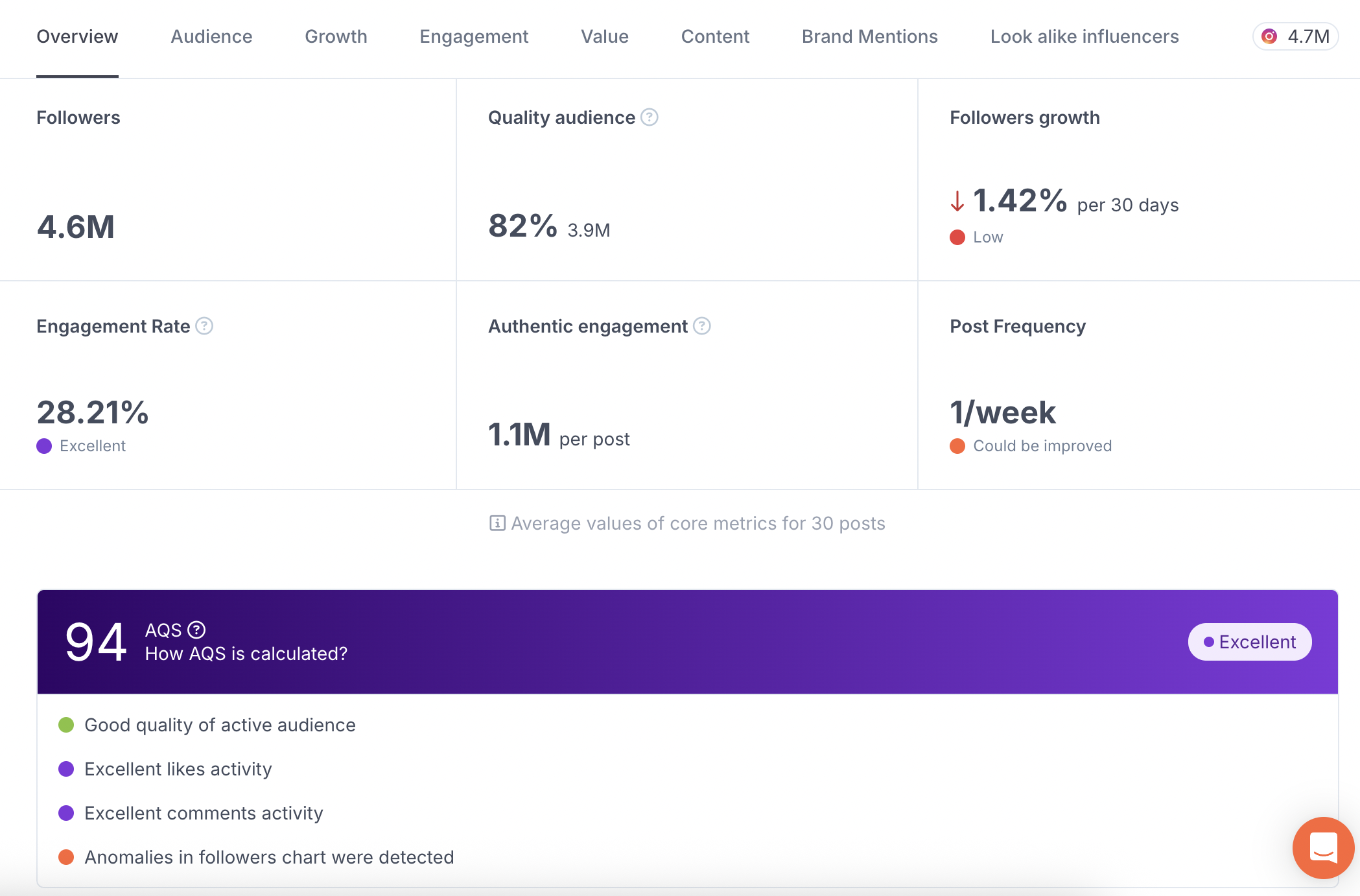 HypeAuditor removes this risk by giving marketers direct access to reliable reports that cannot be edited or fabricated. There, you can see a full influencer report divided into sections that highlight the most important performance metrics.
HypeAuditor removes this risk by giving marketers direct access to reliable reports that cannot be edited or fabricated. There, you can see a full influencer report divided into sections that highlight the most important performance metrics.
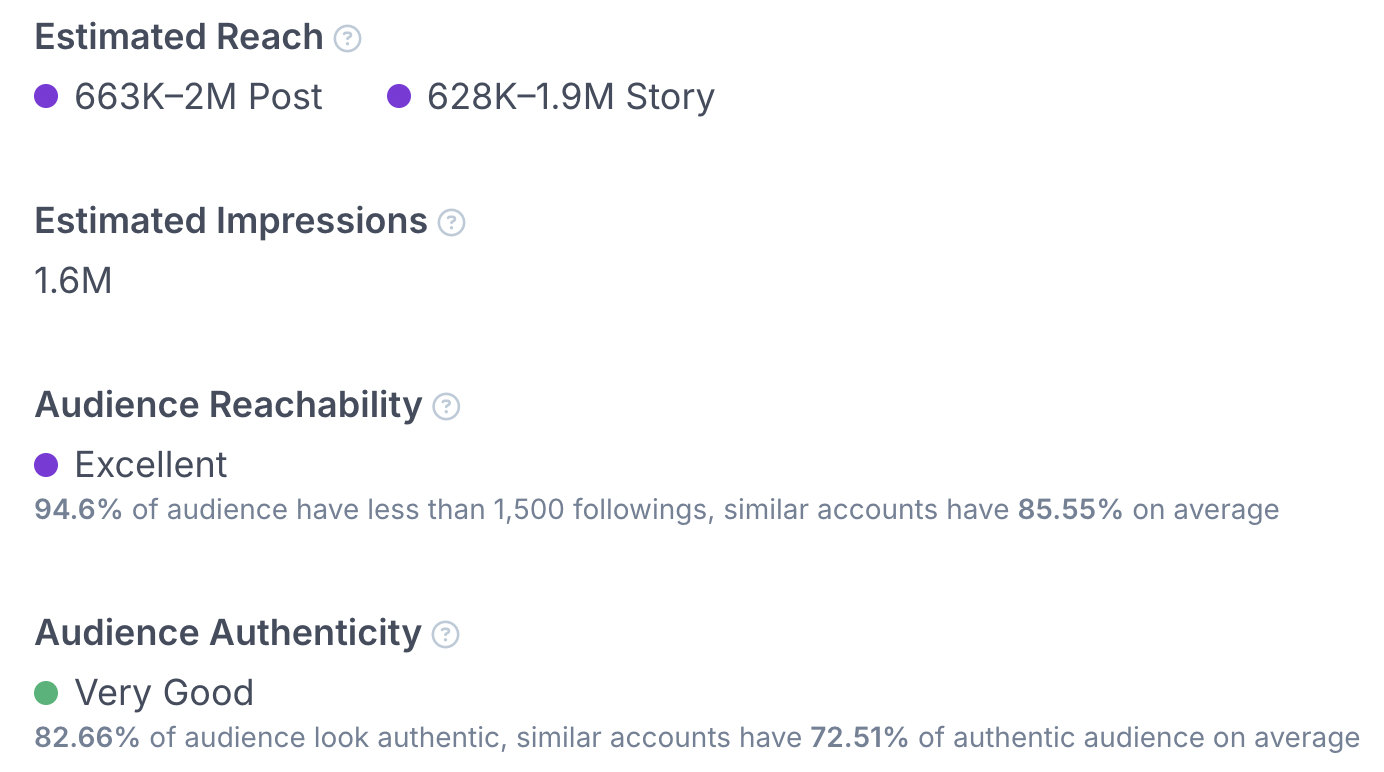 For example, you can track estimated reach and impressions, audience reachability and authenticity, and the performance of advertising posts compared to organic ones. All of this information comes from real data, updated consistently, so marketers know they’re looking at accurate results instead of modified screenshots.
For example, you can track estimated reach and impressions, audience reachability and authenticity, and the performance of advertising posts compared to organic ones. All of this information comes from real data, updated consistently, so marketers know they’re looking at accurate results instead of modified screenshots.
8. Algorithm manipulation
Algorithm manipulation happens when influencers use tricks to force platforms into giving their content more visibility than it deserves. This can be done by paying for automated activity, using bots to blow up engagement, or exploiting loopholes that push posts higher in feeds. Then, you’ll get a profile that looks popular on the surface but lacks genuine influence underneath as a result.
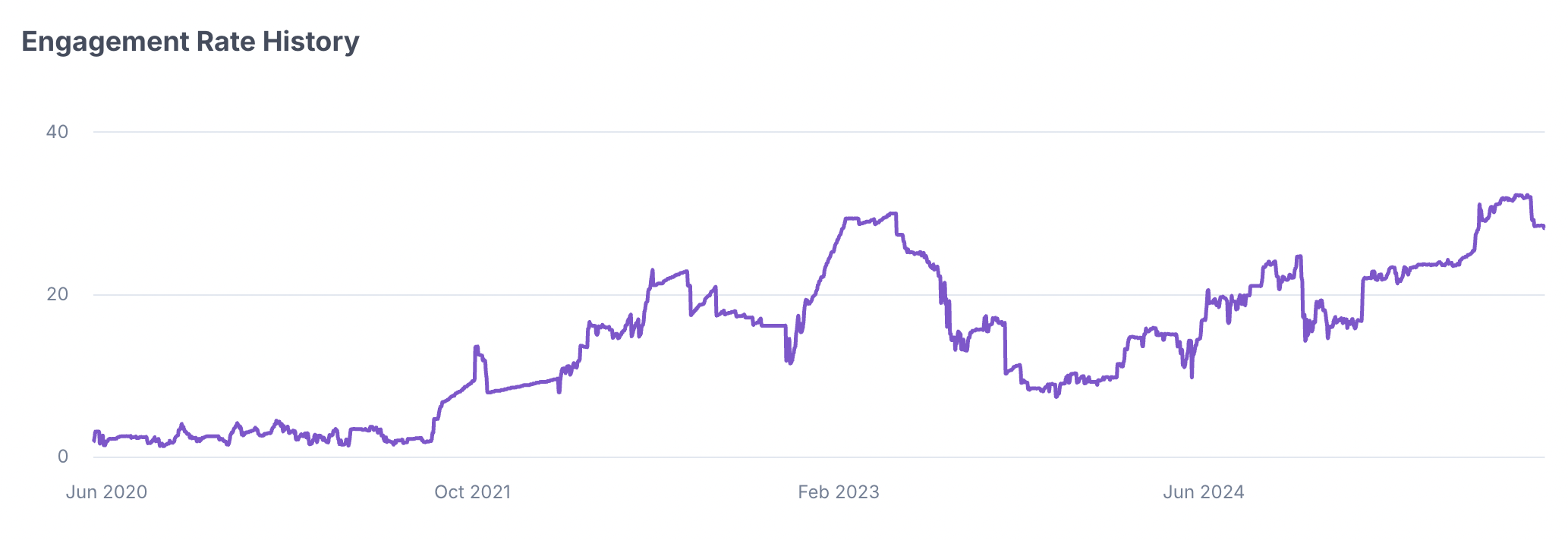 HypeAuditor makes this kind of manipulation easier to detect by tracking engagement over time. The Engagement Rate History graph shows how an influencer’s performance has changed from their earliest posts to their latest ones. A healthy account will show natural rises and falls, but sudden peaks or unnatural consistency maybe a sign of red flags.
HypeAuditor makes this kind of manipulation easier to detect by tracking engagement over time. The Engagement Rate History graph shows how an influencer’s performance has changed from their earliest posts to their latest ones. A healthy account will show natural rises and falls, but sudden peaks or unnatural consistency maybe a sign of red flags.
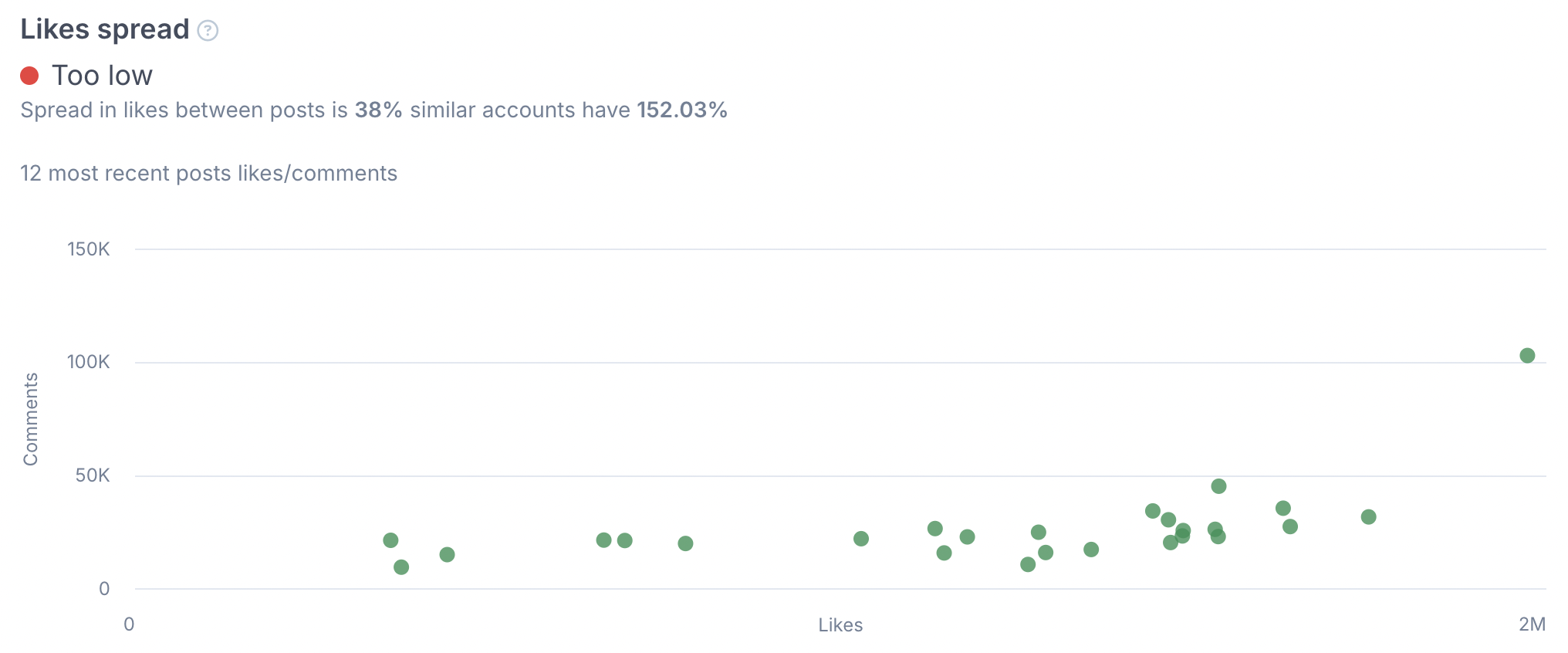 For deeper analysis, HypeAuditor also measures likes spread. Real followers interact differently with each post, so some content should perform better than others. When likes are almost identical across every post, it suggests that artificial methods—such as bought likes—are being used to keep numbers steady. With these insights, marketers can see behind the polished metrics and understand whether an influencer’s popularity is real.
For deeper analysis, HypeAuditor also measures likes spread. Real followers interact differently with each post, so some content should perform better than others. When likes are almost identical across every post, it suggests that artificial methods—such as bought likes—are being used to keep numbers steady. With these insights, marketers can see behind the polished metrics and understand whether an influencer’s popularity is real.
That's how we keep you safe in influencer marketing
Fraud in influencer marketing is present in many forms, from fake followers and manipulated growth to fabricated reports and misleading collaborations. Each of these tactics creates risks for brands and agencies that invest time and resources expecting impactful results.
With HypeAuditor, those risks become easier to spot and eliminate. Its AI-driven analytics combined with detailed reports on audience quality, engagement authenticity, and brand mentions help marketers work with relief knowing they’re making decisions based on valid data, not manipulated signals.
For teams that want safer, more transparent influencer partnerships, HypeAuditor is built to be trusted. It helps you filter out fraud, focus on creators with real audiences, and build campaigns that bring honest results in the most convenient way possible for all marketers. If you’d like to see how this works in practice, reach out to our sales team today for a guided demo.